
- Forum posts: 2
Jan 3, 2019, 2:58:30 PM via Website
Jan 3, 2019 2:58:30 PM via Website
We all hear about Android being a less secure, more vulnerable (or more accurate, malware) platform that attacks and steals data. This information is somewhat correct, but you should not be too worried about the phone you have in your hand. Inside Android, Google has integrated many features to prevent malware, if there is a little more attention from you, making sure our phone is safe is not difficult at all.
Why do people say "Android is less secure"?
Android is an open source platform, this is well known, but not so that it is less secure. Open here is simply open in terms of source code and processes and how the system operates, does not mean that everyone can fix it because the core is still held by Google. Opening does not mean that any software installed on Android has the right to penetrate into the kernel of the operating system to make you mess. In contrast, decentralized software and files are very clear, not want to run and run, what to open is open, similar to many other Linux-based operating systems being used by the world.
The "open" feature that we often mention when talking about Android lies in its comfort in the interface elements, file management, application installation resources, and competitors are directly compared. is iOS. This "open" has nothing to do with opening the source code. Look at Windows, it can do everything Android does, but it's still closed source. And the main problem we're discussing in this topic also revolves around this
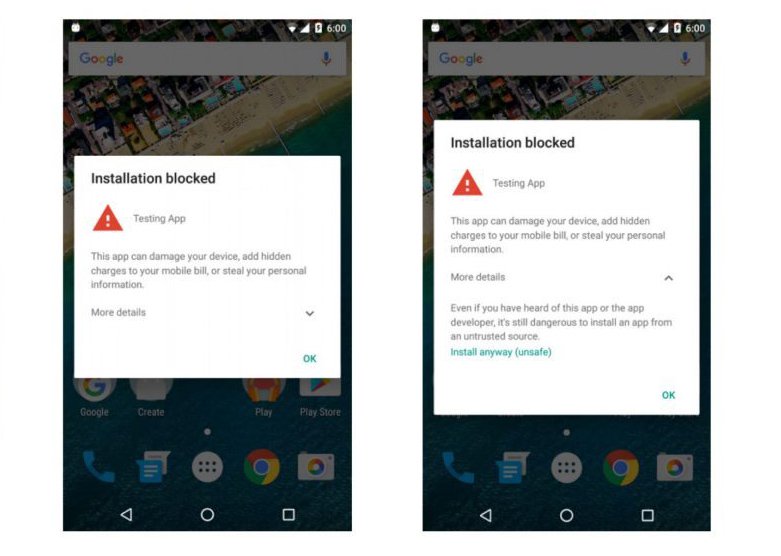
Among the factors that Android gives us comfortable intervention, the "source install" element is the source of many security issues. As you know, any Android user can install an app from Google Play Store - is an official app source and is carefully moderated, or you can install it directly from APK files - the format Run file for Android. Because Android can install app APK very easily, anyone can do it, so they are born third-party app stores, where the app is almost not checked thoroughly before letting users download (except for the store of Amazon) so a bad person can upload an app containing malicious code here and wait for you to download it.
Another way that is used to spread malware to an Android device is the way in which users install the app. Notifications "your phone has a virus, install app XYZ to remove" or "your phone is running slow, install app ABC to get it running fast" are the most common tricks of the hacker. Once you have downloaded the APK file containing the malicious code and installed it on your computer, it is new to know what it is doing and it is exploiting any security hole of Android to attack you.
Another problem that makes Android more vulnerable to attack than iOS is that the update time of Android is too slow, depends a lot on the manufacturer as well as the network. When Apple discovered a flaw, they immediately created a patch and released it to millions of users in a short time. Meanwhile, due to the heavy fragmentation, the Android update often takes weeks, even months, to users. That is the heavy holes that have just been patched like that, with lighter holes, the manufacturer does not set a high priority. Only Nexus or Pixel machines are quickly updated because of Google's "home chick", others also only have the newly patched high-end flagship. There are many old devices that are sometimes not updated.
But should be too worried?
Do not need. Google knows the nature of its operating system fragmentation, so it has come up with many anti-malware measures available in the platform, and any Android device will have the security features below. Of course they will depend on the Android version, I will tell you if the feature depends on the version.
By default Google turns off the app settings from outside, only for installing from Play Store. This is the first barrier that Google has built to combat malware. As mentioned above, the Play Store app is much safer than the floating app that you install from an unclear source. If someone intends to upload an app containing malicious code, Google has blocked it from the beginning. So if not really necessary, you should not turn on the mode to allow installing apps from outside. I know that many high-end users who do not play games do not turn on this mode to do anything.
Since Android 4.2 Jelly Bean, Google integrates the Verify Apps feature. This can be seen as a firewall that filters out malicious apps even if it has been installed on your computer. Verify Apps works like anti-virus software on your computer: every time you install an app, Verify Apps will search to see if it has malicious code, exploit any security holes, and have a name on the list. Black book of Google or not. If so, the app will be stopped immediately with the "Installation has been blocked." In some cases, Verify Apps will only warn users, and if you wish, you can still accept the risk to continue the installation.
Verify Apps also comes from its use of Google Play Services' information, a background service in Android that performs many functions, including a feature that helps Verify Apps detect malware. Google Play Services is updated very often so you can be assured.
3. The Android device is not rooted by default. Root is the highest access of all Linux operating systems, when the app has root access, it means it can interfere deeply with the system and do whatever it wants. Therefore, by default, no manufacturer has to root its device. We are often rooted by the brothers, do it by themselves. Without root, the malicious application cannot run processes freely, unable to sneak the camera, recorder or phone, nor can it spread to other apps.
Recommended editorial content
With your consent, external content is loaded here.
By clicking on the button above, you agree that external content may be displayed to you. Personal data may be transmitted to third-party providers in the process. You can find more information about this in our Privacy Policy.